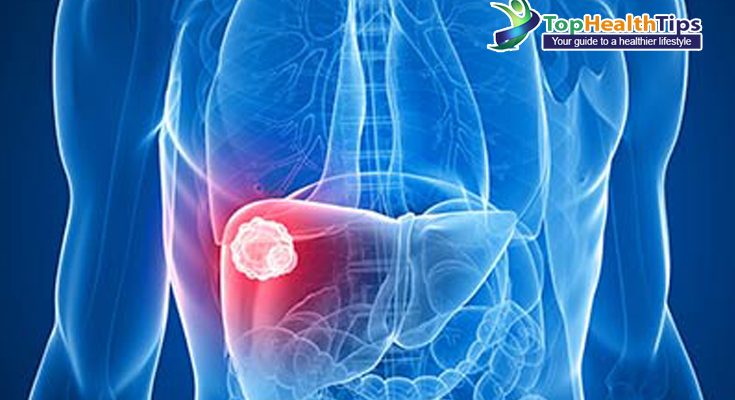
Liver cancer, also known as hepatic cancer, is a serious and often aggressive form of cancer that originates in the liver. Given its critical role in detoxifying the body and aiding in digestion, the health of the liver is crucial to overall well-being. This article explores the causes, symptoms, and potential remedies for liver cancer, aiming to provide a comprehensive understanding of this challenging disease.
What is Liver Cancer?
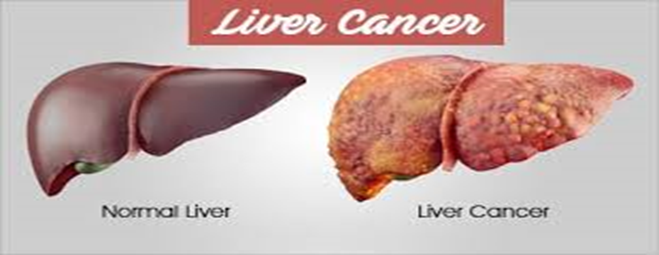
Liver cancer starts when abnormal cells in the liver grow uncontrollably. It can be primary, originating in the liver itself, or secondary, meaning it has spread from another part of the body. The most common type of primary liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which starts in the liver cells.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Several factors can increase the risk of developing liver cancer, including:
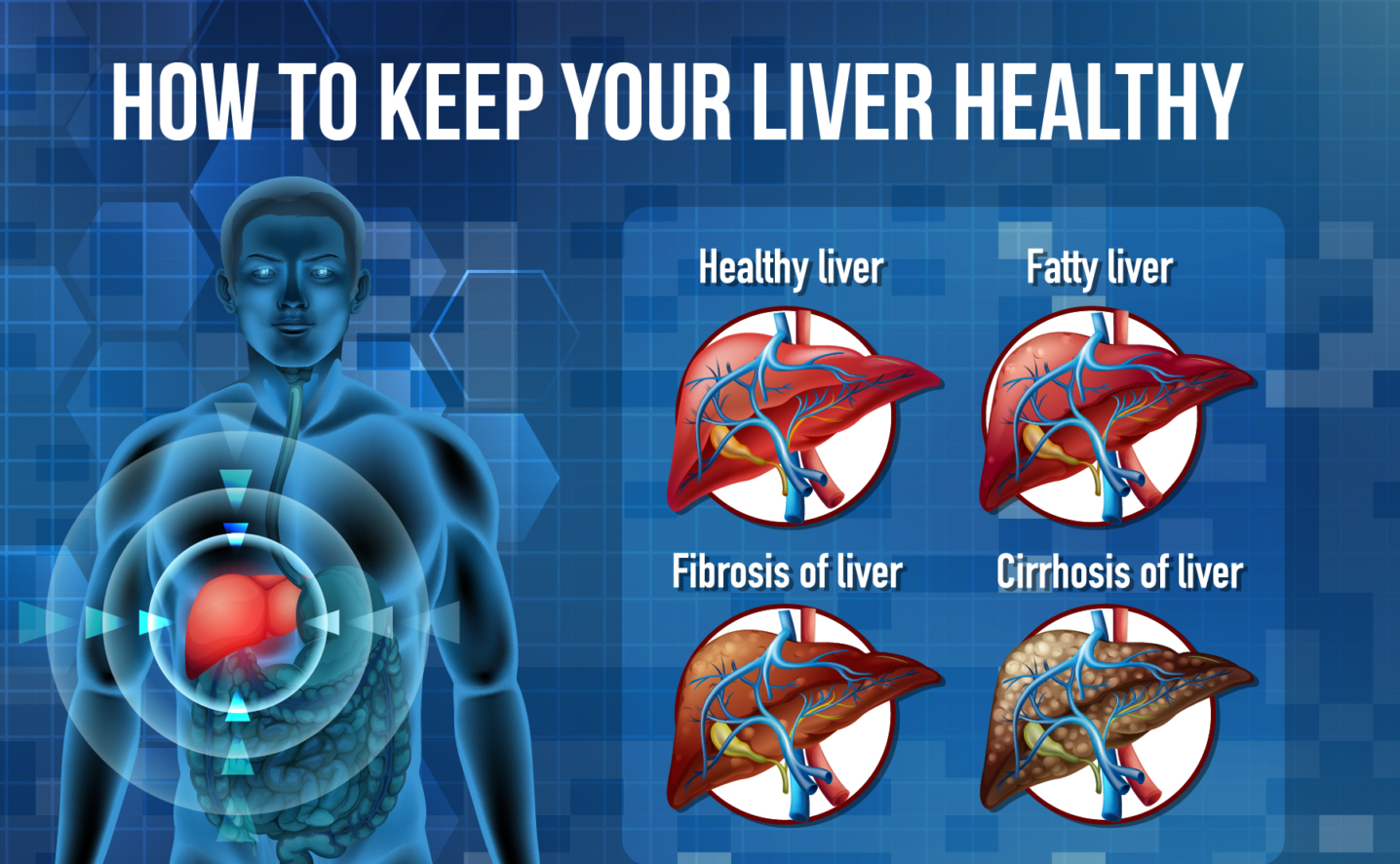
- Chronic Liver Disease: Long-term liver conditions such as cirrhosis, hepatitis B or C infections, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) can lead to liver cancer. Chronic inflammation and liver damage increase the risk.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can lead to liver cirrhosis, which is a significant risk factor for liver cancer.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can contribute to the development of fatty liver disease, which may progress to cirrhosis and increase cancer risk.
- Hepatitis Infections: Chronic infection with hepatitis B or C viruses is a major risk factor for liver cancer. These viruses can cause long-term inflammation and damage to the liver.
- Genetic Factors: Certain genetic conditions and family history of liver cancer may increase susceptibility.
- Aflatoxin Exposure: Aflatoxins are toxins produced by certain molds that can contaminate crops. Chronic exposure to aflatoxins is linked to liver cancer, particularly in parts of the world where these molds are common.
Symptoms of Liver Cancer:
Early liver cancer often does not cause noticeable symptoms, which makes it difficult to diagnose in its initial stages. As the disease progresses, symptoms may include:
- Abdominal Pain: Discomfort or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Sudden loss of weight without a clear reason.
- Loss of Appetite: Reduced interest in eating, sometimes accompanied by nausea.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes due to elevated bilirubin levels.
- Swollen Abdomen: Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, known as ascites.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness or weakness.
- Itchy Skin: Generalized itching due to bile buildup.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing liver cancer typically involves a combination of methods:

- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRIs can help visualize tumors and assess their size and location.
- Blood Tests: Liver function tests and tumor markers such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) can indicate liver abnormalities.
- Biopsy: A sample of liver tissue may be obtained through a needle biopsy or during surgery to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Remedies and Treatment Options:
Treatment for liver cancer depends on the stage of the disease, the patient’s overall health, and whether the cancer is primary or secondary. Options include:
- Surgery: If the cancer is localized and the liver function is adequate, surgical options such as partial hepatectomy (removal of a portion of the liver) or liver transplantation may be considered.
- Ablation Therapy: Techniques like radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or microwave ablation use heat to destroy cancer cells. These methods are generally used for small tumors.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that target specific molecules involved in cancer growth may be used to treat liver cancer. These therapies can help slow the progression of the disease.
- Chemotherapy: While less common for liver cancer due to limited effectiveness, chemotherapy may be used in some cases, especially for secondary liver cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy radiation can be used to target and destroy cancer cells. It is often used when surgery is not an option.
- Immunotherapy: This emerging treatment helps the body’s immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. It is an area of ongoing research and may be an option for some patients.
Lifestyle and Dietary Remedies:

While conventional treatments are crucial, supportive lifestyle changes and dietary measures can improve overall health and quality of life:
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains supports liver health. Avoiding alcohol and processed foods is essential.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and can improve overall well-being.
- Managing Hepatitis: If hepatitis B or C is present, following prescribed antiviral treatments can help manage the disease and reduce cancer risk.
- Avoiding Toxins: Reducing exposure to harmful substances, such as aflatoxins and environmental toxins, is important for liver health.
Alternative remedy for liver cancer:

While conventional treatments for liver cancer such as surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies are crucial, some individuals explore alternative or complementary remedies to support their health and well-being during treatment. It’s important to note that alternative remedies should not replace conventional medical care but can be used in conjunction with it to enhance overall health and potentially improve outcomes. Here’s a look at some alternative remedies that are sometimes considered:
1. Dietary Adjustments:

- Anti-Cancer Foods: Incorporating foods with anti-cancer properties, such as cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower), berries, and turmeric, may support overall health and potentially have protective effects. These foods contain antioxidants and compounds that may help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Detoxification Foods: Foods that support liver function and detoxification, such as leafy greens, beets, garlic, and ginger, can be beneficial. These foods may help enhance liver health and support the body’s natural detoxification processes.
- Avoiding Processed Foods: Reducing intake of processed and sugary foods can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce inflammation, which is beneficial for overall health.
2. Herbal Remedies:

- Milk Thistle: Known for its active ingredient silymarin, milk thistle is often used to support liver health. Some studies suggest it may have protective effects on liver cells and improve liver function.
- Artichoke Extract: Artichoke has been studied for its potential liver-protective properties. It may help stimulate bile production and support liver function.
- Green Tea: Rich in antioxidants, particularly catechins, green tea may have protective effects on liver cells and support overall liver health.
- Ginger: Ginger is known for its anti-inflammatory properties and may help alleviate symptoms such as nausea and support digestive health.
3. Lifestyle Changes:

- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can improve overall health, support weight management, and potentially enhance the effectiveness of conventional treatments.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga can help manage stress, improve emotional well-being, and potentially support immune function.
4. Complementary Therapies:

- Acupuncture: Some individuals find relief from symptoms such as pain and nausea through acupuncture. It may help improve overall quality of life and support conventional treatments.
- Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can help reduce stress, alleviate pain, and improve circulation. It’s important to ensure that the massage therapist is experienced in working with cancer patients.
5. Supportive Supplements

- Vitamin D: Maintaining adequate levels of vitamin D is important for overall health. Some studies suggest that vitamin D may have a role in cancer prevention and support immune function.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil and flaxseed oil, omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties and may support overall health.
6. Homeopathy remedy:

Here are some homeopathic remedies that are considered for liver cancer as per symptoms.:
- Chelidonium majus: Used for liver ailments with symptoms like right-sided pain, jaundice, and digestive issues.
- Carduus marianus: Commonly prescribed for liver and gallbladder problems, especially when there’s discomfort and inflammation.
- Lycopodium clavatum: Often used for digestive disturbances and liver complaints, particularly when there is bloating and a feeling of fullness.
- Nux vomica: Considered for liver congestion and digestive issues, often related to overindulgence or stress.
- Phosphorus: Sometimes used for liver conditions with symptoms such as weakness, fatigue, and digestive issues.
- Arsenicum album: Used for liver issues with symptoms of weakness, exhaustion, and a general sense of being unwell.
- Silybum marianum: Derived from milk thistle, sometimes used for liver support, though its use is more common in herbal medicine.
- Hepar sulphuris: Sometimes considered for liver complaints with symptoms like sharp, shooting pains and sensitivity.
- Bovista: Used for liver conditions associated with a sense of fullness and heaviness in the abdomen.
- Sulphur: May be used for general liver discomfort, especially if there are symptoms of heat or irritation.
Important Considerations:

- Consult Healthcare Providers: Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any alternative remedy or supplement. They can help ensure that these approaches do not interfere with conventional treatments or medications.
- Evidence and Safety: Many alternative remedies have limited scientific evidence supporting their efficacy. It’s important to rely on treatments that have been proven effective through rigorous research and to use alternative remedies as complementary options.
- Integrated Care: Working with a healthcare team that includes oncologists, nutritionists, and other specialists can help create a comprehensive care plan that addresses all aspects of health and well-being.
Conclusion:
Liver cancer is a serious condition with complex treatment options and significant impacts on health. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and available treatments can empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health. Early detection and a comprehensive treatment approach, including both medical interventions and lifestyle adjustments, are key to improving outcomes and quality of life for those affected by liver cancer.