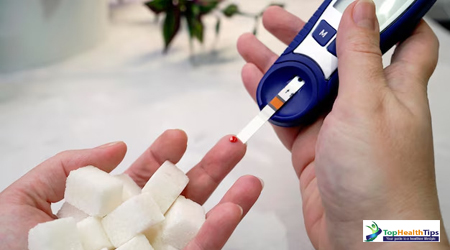
Diabetes is a growing concern worldwide, with millions of people at risk of developing this chronic condition. Recognizing the early signs of diabetes can help in timely diagnosis and effective management, potentially preventing severe complications. In this article, we will explore 10 early signs of diabetes you should never ignore. Understanding these signs can be your first step towards better health.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Diabetes
- Why Recognize Early Signs?
- 10 Early Signs of Diabetes
- Excessive Thirst
- Frequent Urination
- Unexplained Weight Loss
- Fatigue and Weakness
- Blurred Vision
- Increased Hunger
- Slow Healing Wounds
- Tingling or Numbness
- Darkened Skin Patches
- Frequent Infections
- Table: Early Signs of Diabetes and Their Explanations
- Prevention and Management Tips
- Lifestyle Adjustments for Better Control
- When to See a Doctor
- Conclusion
- References
1. Introduction to Diabetes
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels, either due to insufficient insulin production or improper utilization of insulin by the body. It primarily includes two types:
- Type 1 Diabetes: The immune system attacks insulin-producing cells, leading to a lack of insulin in the body. This type usually manifests in children and young adults.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The body becomes resistant to insulin, making it harder for cells to absorb glucose. This type is more common among adults, especially those who are overweight or have a sedentary lifestyle.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 422 million people globally suffer from diabetes, and the prevalence continues to rise. Early detection of diabetes can prevent complications like heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems.
2. Why Recognize Early Signs?
Identifying early symptoms of diabetes allows for prompt medical intervention, potentially delaying or preventing progression to more severe stages. Early management through lifestyle changes or medication can significantly improve a person’s quality of life. Recognizing these symptoms is also crucial because:
- Prevention: Early intervention can prevent the transition from prediabetes to Type 2 diabetes.
- Improved Management: Early detection allows for a more personalized management plan.
- Cost Savings: Treating diabetes at an advanced stage can be expensive. Early diagnosis can save on long-term medical costs.
- Quality of Life: Addressing symptoms early can prevent severe complications, improving overall well-being.
3. 10 Early Signs of Diabetes

1. Excessive Thirst (Polydipsia)
One of the most common symptoms, excessive thirst, occurs as the body attempts to compensate for the high levels of glucose in the bloodstream. This symptom often pairs with frequent urination. When blood sugar levels rise, the kidneys must filter out the excess glucose, leading to dehydration.
- Example: Sarah, a 45-year-old woman, found herself constantly thirsty, even after drinking several glasses of water. Despite the cold weather, she needed water frequently. After a visit to her doctor, she discovered it was an early sign of Type 2 diabetes.
2. Frequent Urination (Polyuria)
Increased blood sugar levels cause the kidneys to work harder to filter and absorb the excess glucose. This process results in more urine production, leading to frequent urination, especially during the night.
- Example: For John, waking up three to four times a night to use the bathroom became the new normal. He initially thought it was due to his increased water intake, but his doctor diagnosed him with diabetes.
3. Unexplained Weight Loss
Despite eating more than usual, individuals with diabetes may experience significant weight loss. The body, unable to use glucose for energy, starts breaking down muscle and fat for fuel. This unintentional weight loss is a red flag, especially if it occurs over a short period.
- Scientific Insight: The lack of insulin prevents glucose from entering cells, so the body breaks down protein and fat instead, resulting in weight loss.

4. Fatigue and Weakness
Persistent fatigue is common as the body struggles to convert sugar into energy. This symptom can be easily mistaken for general tiredness but should not be ignored if it persists. Diabetic fatigue is caused by fluctuating blood sugar levels and dehydration.
- Practical Tip: If fatigue continues despite sufficient sleep and a balanced diet, consult a healthcare professional for blood sugar testing.
5. Blurred Vision
High blood sugar levels can cause the lenses in the eyes to swell, leading to blurred vision. If untreated, this can progress to more serious eye conditions like diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic eye issues are a leading cause of blindness in adults.
- Example: Mary noticed her vision becoming blurry, making it difficult to read. A check-up revealed that high blood sugar levels were affecting the shape of her eye lenses.
6. Increased Hunger (Polyphagia)
People with diabetes often feel excessively hungry as their cells are unable to absorb glucose properly. This results in the body signaling for more food, even after a recent meal. It can also contribute to weight gain if not managed properly.
- Scientific Insight: Polyphagia occurs when insulin resistance prevents glucose from reaching the cells, signaling the brain that more energy is needed.
7. Slow Healing Wounds
High blood sugar levels impair circulation and slow down the healing process of cuts and sores. This can lead to an increased risk of infections, especially on the feet, which can become serious if untreated.
- Practical Tip: Keep a close eye on minor cuts and scrapes. If they take longer than usual to heal, it might be time to get your blood sugar levels checked.
8. Tingling or Numbness (Peripheral Neuropathy)
Persistent high blood sugar levels can damage nerves, especially in the extremities. This causes a tingling sensation or numbness in the hands and feet, a condition known as peripheral neuropathy. It can progress to pain and loss of sensation if not addressed early.
- Example: James, a 55-year-old, felt a persistent tingling in his feet, which he initially dismissed as age-related. It turned out to be an early sign of diabetes-induced nerve damage.
9. Darkened Skin Patches (Acanthosis Nigricans)
Dark, velvety patches of skin, especially around the neck, armpits, or groin, can indicate insulin resistance, a common precursor to diabetes. This condition is more common in individuals with darker skin tones.
- Practical Tip: If you notice new patches of darkened skin, it’s advisable to consult a dermatologist or endocrinologist for further evaluation.
10. Frequent Infections
People with diabetes are more prone to infections, including skin infections, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and yeast infections. This is due to weakened immune function caused by elevated blood sugar levels.
- Scientific Insight: High glucose levels provide an environment where bacteria and fungi can thrive, increasing susceptibility to infections.
Table: Early Signs of Diabetes and Their Explanations
| Sign | Description |
|---|---|
| Excessive Thirst | Caused by dehydration due to increased urination as kidneys work to eliminate excess sugar. |
| Frequent Urination | High blood glucose levels lead to more urine production, causing frequent trips to the bathroom. |
| Unexplained Weight Loss | The body breaks down fat and muscle for energy due to the inability to utilize glucose properly. |
| Fatigue | Lack of energy as the body struggles to convert glucose into fuel, leading to persistent tiredness. |
| Blurred Vision | High sugar levels cause swelling in the eye lenses, distorting vision. |
| Increased Hunger | Cells are deprived of glucose, triggering hunger signals despite recent meals. |
| Slow Healing Wounds | Impaired circulation and reduced healing capability due to high blood sugar levels. |
| Tingling or Numbness | Nerve damage caused by prolonged high blood sugar, affecting the hands and feet. |
| Darkened Skin Patches | Insulin resistance often manifests as dark, velvety patches in body folds. |
| Frequent Infections | High glucose levels weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections. |
4. Prevention and Management Tips
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, and vegetables. Avoid processed foods and high-sugar beverages.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity helps manage weight and improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
- Regular Check-ups: Monitor blood sugar levels and consult your doctor for routine screenings. Early detection can lead to better outcomes.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to support kidney function and reduce the risk of dehydration.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can increase blood sugar levels. Practice relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.
5. Lifestyle Adjustments for Better Control
Making small lifestyle changes can have a significant impact on diabetes management:
- Mindful Eating: Pay attention to portion sizes and carbohydrate intake.
- Sleep Hygiene: Quality sleep helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- Limit Alcohol: Excessive alcohol can interfere with blood sugar levels.
- Support System: Join diabetes support groups to stay motivated and informed.
6. When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of the above symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. They may recommend a blood glucose test to confirm if you have diabetes or prediabetes. Early intervention can make a significant difference in managing this condition effectively.
- Questions to Ask Your Doctor:
- What type of diabetes do I have?
- How often should I check my blood sugar?
- What lifestyle changes can help manage my condition?
7. Conclusion
Recognizing the early signs of diabetes is crucial for timely intervention and better management. If you notice symptoms like excessive thirst, frequent urination, or unexplained weight loss, seek medical advice immediately. With a proactive approach, managing diabetes becomes more achievable, improving overall health and well-being.
Related posts for Disease & Remedy>>>
8. References
- American Diabetes Association. (2024). Diabetes Symptoms. Retrieved from www.diabetes.org
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Symptoms of Diabetes. Retrieved from www.mayoclinic.org
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2024). Diabetes Overview. Retrieved from www.niddk.nih.gov
- World Health Organization. (2024). Global Report on Diabetes. Retrieved from www.who.int
- Harvard Medical School. (2024). Managing Blood Sugar Levels. Retrieved from www.health.harvard.edu